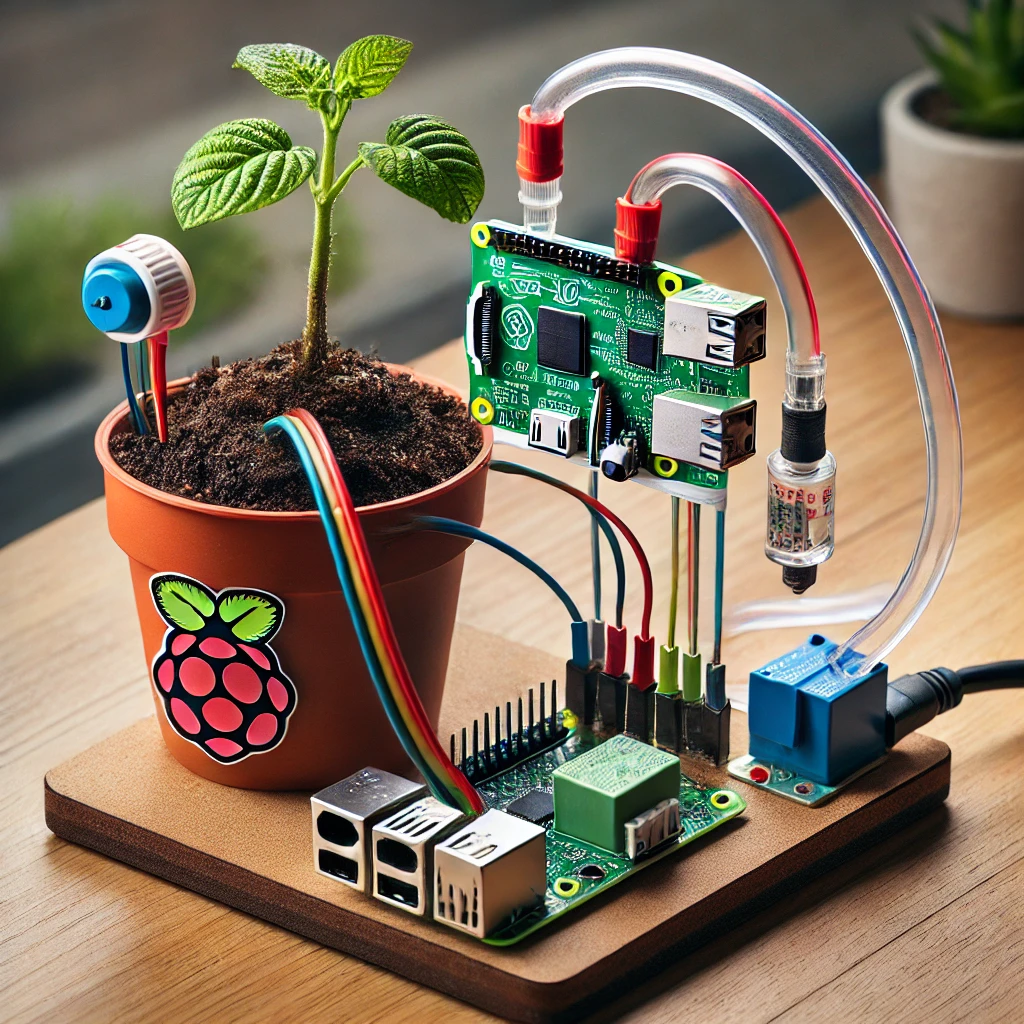
Keeping your plants healthy and hydrated can be challenging, especially when you’re away from home or caught up in a busy schedule. Fortunately, with the power of the Raspberry Pi Pico, you can create an automatic plant-watering system that ensures your plants receive the right amount of water, even when you’re not around. This DIY project is perfect for gardening enthusiasts and tech hobbyists alike.
Materials Needed:
- Raspberry Pi Pico
- Soil Moisture Sensor
- Water Pump
- Relay Module
- Jumper Wires
- Breadboard
- Power Supply
- Water Reservoir
- Tubing
Step-by-Step Guide:
Step 1: Set Up the Raspberry Pi Pico Start by setting up your Raspberry Pi Pico. If you haven’t already, download and install the MicroPython firmware onto your Pico. Connect your Pico to your computer using a USB cable, and open your preferred IDE, such as Thonny.
Step 2: Connect the Soil Moisture Sensor The soil moisture sensor is the key component that will determine whether your plants need water. Connect the sensor to the Raspberry Pi Pico using jumper wires. The sensor typically has three pins: VCC, GND, and Data. Connect VCC to the 3.3V pin on the Pico, GND to a ground pin, and Data to one of the GPIO pins (e.g., GP28).
Step 3: Connect the Water Pump The water pump will be controlled by the Raspberry Pi Pico via a relay module. Connect the relay module to the Pico, then wire the water pump to the relay. Ensure the pump is also connected to a water reservoir using tubing.
Step 4: Write the Python Code Now, it’s time to program your Raspberry Pi Pico to control the plant-watering system. The code will read the soil moisture sensor’s data and activate the water pump when moisture levels fall below a certain threshold.
python
from machine import Pin, ADC
import timesoil_moisture_sensor = ADC(Pin(28))
water_pump_relay = Pin(16, Pin.OUT)
MOISTURE_THRESHOLD = 30000
moisture_level = soil_moisture_sensor.read_u16()
water_pump_relay.on()
time.sleep(5) # Water for 5 seconds
water_pump_relay.off()
else:
water_pump_relay.off()
Step 5: Test the System Once your code is ready, upload it to the Raspberry Pi Pico. Test the system by placing the soil moisture sensor in the soil and filling the reservoir with water. Monitor how the system responds to changes in soil moisture.
Step 6: Finalize and Deploy After successful testing, you can mount the components into a waterproof container or directly in your garden. Ensure the water pump is securely connected to the water source and the tubing leads to the plants.