In a world where technology continues to break barriers, the Raspberry Pi has become a cornerstone for innovative solutions. One of the most remarkable advancements is the Raspberry Pi-powered “third eye,” designed to aid visually impaired individuals in navigating their surroundings with the help of artificial intelligence (AI). This groundbreaking device opens up new possibilities for accessibility and independence, providing a safer and more intuitive experience for those who need it most.
How the ‘Third Eye’ Works
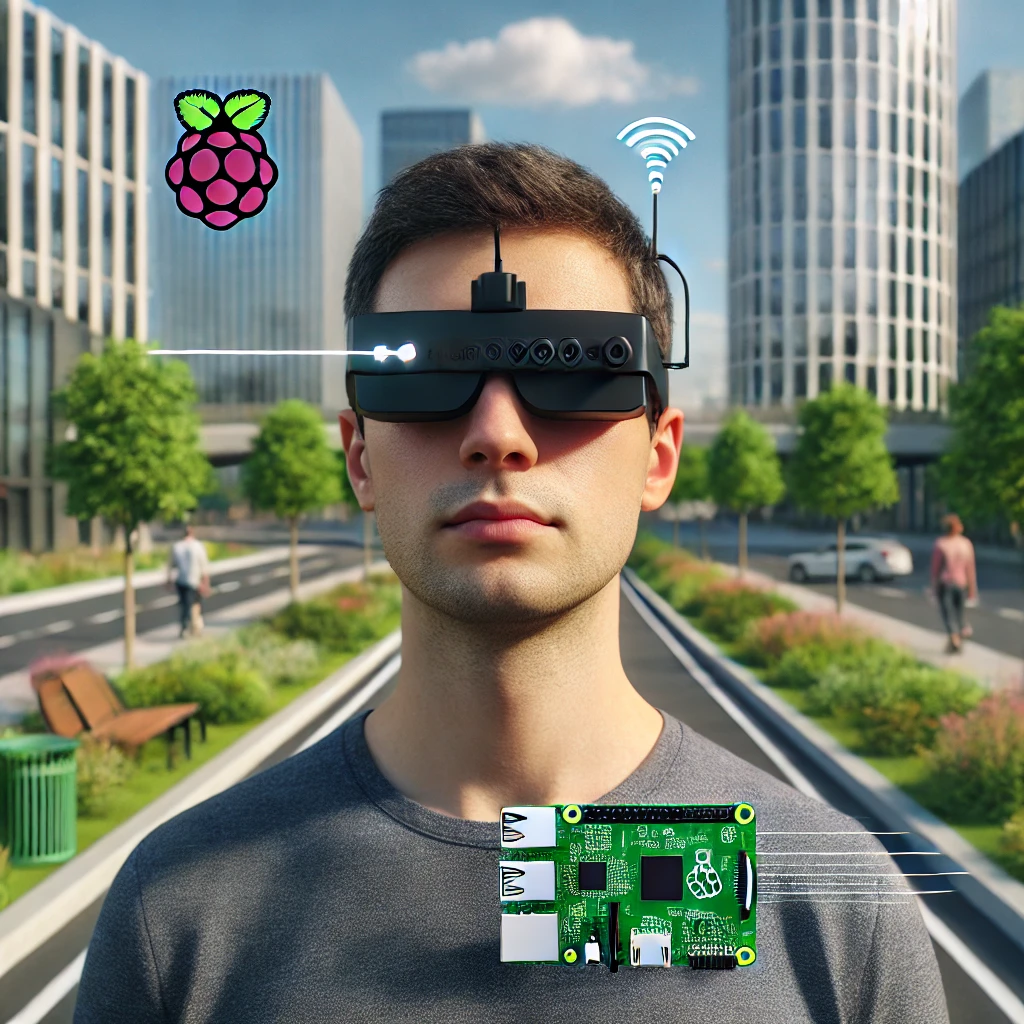
The ‘third eye’ is a compact, wearable device powered by a Raspberry Pi, which integrates with advanced AI algorithms to interpret the environment. The device uses a combination of sensors, cameras, and machine learning models to detect obstacles, identify objects, and provide real-time feedback to the user through auditory or haptic signals.
Key Features
- AI-Powered Object Recognition: The device can identify common objects like chairs, doors, and stairs, alerting the user to their presence and location.
- Obstacle Detection: Using ultrasonic sensors, the ‘third eye’ can detect obstacles and warn the user before they come too close, helping to prevent accidents.
- Customizable Feedback: Users can choose between different types of feedback, such as voice commands or vibrations, to suit their preferences.
Benefits for the Visually Impaired
The ‘third eye’ offers numerous benefits, including increased independence, improved safety, and a greater sense of confidence in unfamiliar environments. It also represents a cost-effective alternative to more expensive assistive technologies, making it accessible to a wider audience.
Conclusion
The Raspberry Pi-powered ‘third eye’ is a testament to the potential of combining affordable hardware with cutting-edge AI. As technology continues to evolve, devices like this will play a crucial role in enhancing the lives of visually impaired individuals, offering them new ways to experience the world around them.